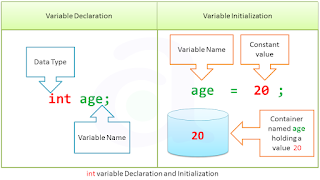
When the variables in the example above are declared, they have an undetermined value until they are assigned a value for the first time. But it is possible for a variable to have a specific value from the moment it is declared. This is called the initialization of the variable.
In C++, there are three ways to initialize variables. They are all equivalent and are reminiscent of the evolution of the language over the years:
The first one, known as c-like initialization (because it is inherited from the C language), consists of appending an equal sign followed by the value to which the variable is initialized:
type identifier = initial_value;
For example, to declare a variable of type
int called x and initialize it to a value of zero from the same moment it is declared, we can write: |
|
A second method, known as constructor initialization (introduced by the C++ language), encloses the initial value between parentheses (
()):type identifier (initial_value);
For example:
|
|
Finally, a third method, known as uniform initialization, similar to the above, but using curly braces (
{}) instead of parentheses (this was introduced by the revision of the C++ standard, in 2011):type identifier {initial_value};
For example:
|
|
All three ways of initializing variables are valid and equivalent in C++.
|